PPT CHAPTER 2 Economic Models Tradeoffs and Trade PowerPoint
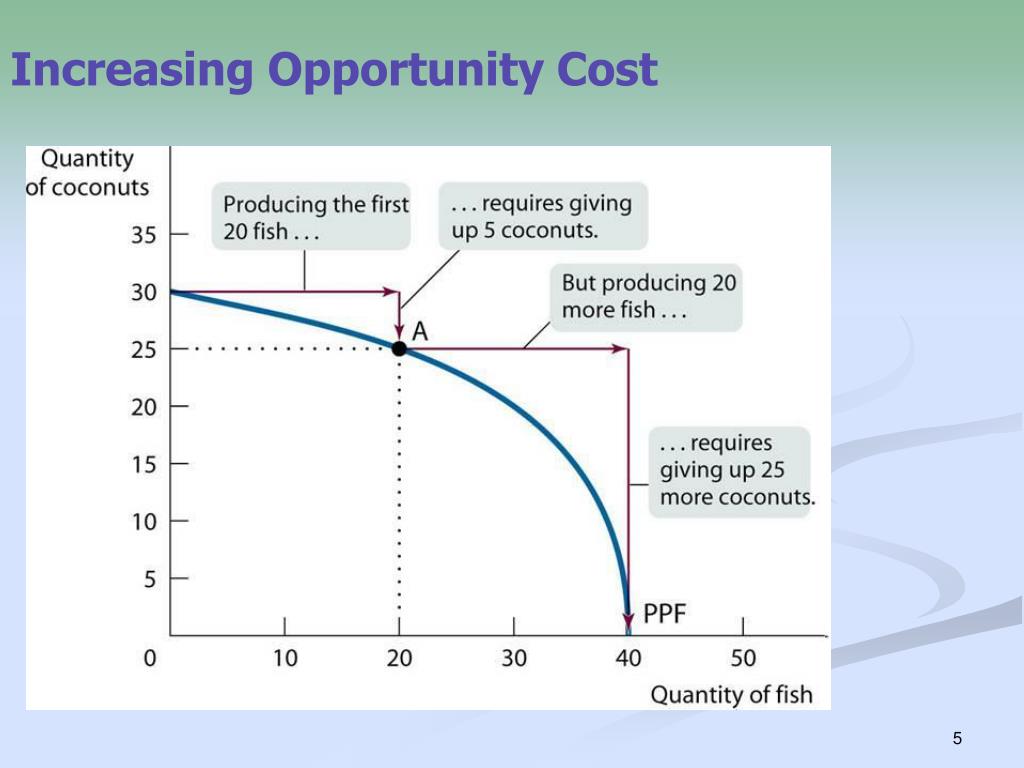
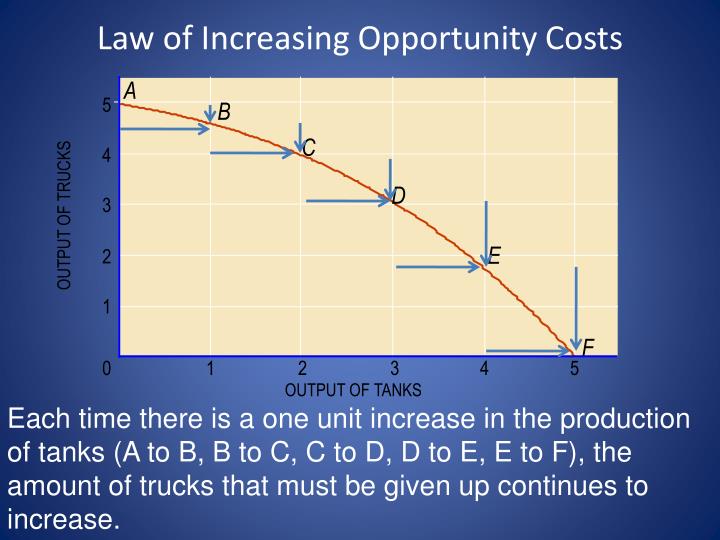
The fact that the opportunity cost of additional snowboards increases as the firm produces more of them is a reflection of an important economic law. The law of increasing opportunity cost holds that as an economy moves along its production possibilities curve in the direction of producing more of a particular good, the opportunity cost of.
PPT Chapter 1 What is Economics About PowerPoint Presentation, free

Plant 3 would be the last plant converted to ski production. There, 50 pairs of skis could be produced per month at a cost of 100 snowboards, or an opportunity cost of 2 snowboards per pair of skis. The bowed-out production possibilities curve for Alpine Sports illustrates the law of increasing opportunity cost.
Solved The law of increasing opportunity costs states that

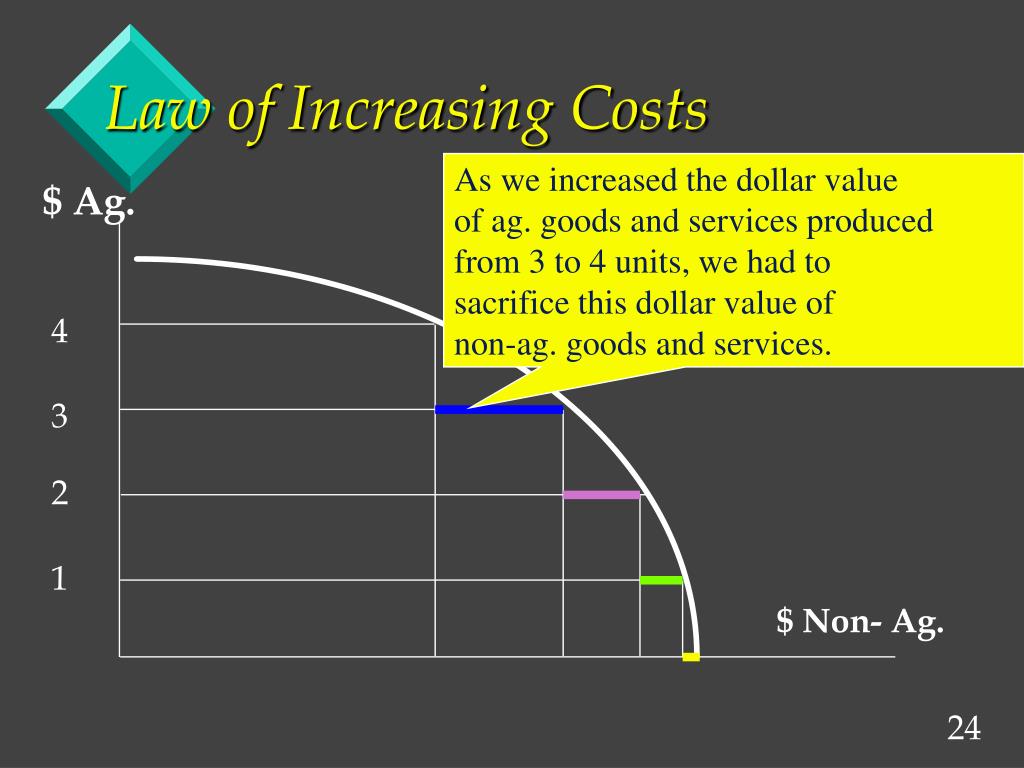
According to the law of increasing opportunity cost, as a society produces more and more of a certain good, further production increases involve ever-greater opportunity costs. As a result, producing the good is associated with greater and greater trade-offs.
PPT Chapter 1 Alleviating Human Misery PowerPoint Presentation ID

The law of increasing opportunity cost is an economic principle that says opportunity costs increase as you allocate resources to the production of each additional alternative unit. This can arise when it's necessary for businesses with limited resources to choose between the production of two different goods. The assumption behind this.
PPT Production Possibilities PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost says that when a person, business, or other entity continues on a particular course of action, the opportunity cost for that action will continually increase.
PPT CHAPTER 1 LIMITS, ALTERNATIVES, AND CHOICES PowerPoint
Business. Economics. Economics questions and answers. According to the law of increasing opportunity costs, A. The more one is willing to pay for resources, the smaller will be the possible level of production. B. Increasing the production of a particular good will cause the price of the good to remain constant. C.
PPT Concept of Opportunity Cost PowerPoint Presentation, free

According to the law of increasing opportunity costs, A. the more one is willing to pay for resources, the small will be the possible level of production B. in order to produce additional units of a particular good, it is necessary for society to sacrifice increasingly larger amounts of alternative goods C. as price rises, suppliers are willing to supply additional output D.increasing the.
Increasing vs Constant Opportunity Cost Economics Capital Flow
According to the law of increasing opportunity costs: a. Greater production leads to greater inefficiency.. Increasing opportunity costs will occur with greater tank production. D. When an economy is producing efficiently it is: a. Producing a combination of goods and services beyond the production-possibilities curve. b. Getting the most.
PPT Chapter 2 Production Possibilities and Opportunity Cost

According to the law of increasing opportunity costs, A. the more one is willing to pay for resources, the smaller will be the possible level of production B. increasing the production of a particular good will cause the price of the good to remain constant C.
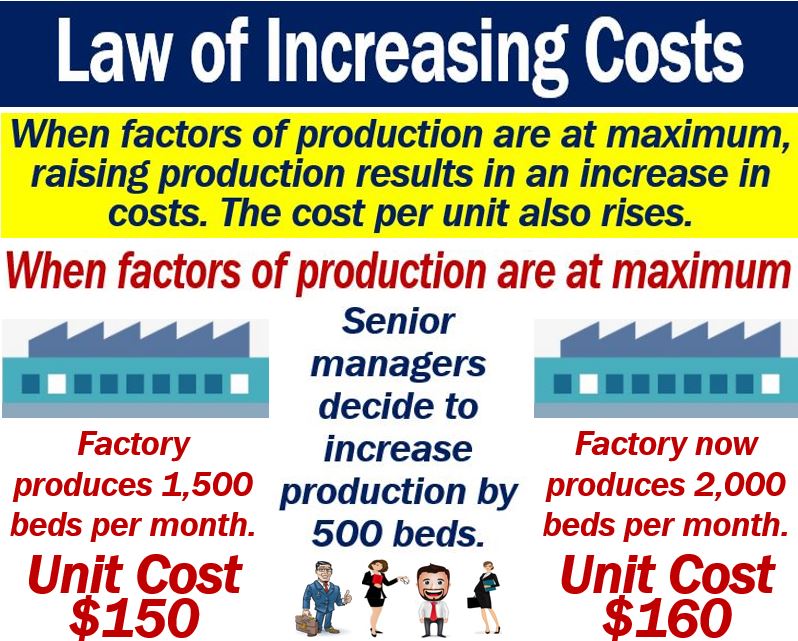
Law of increasing costs definition and examples Market Business News
There, 50 pairs of skis could be produced per month at a cost of 100 snowboards, or an opportunity cost of 2 snowboards per pair of skis. The bowed-out shape of the production possibilities curve illustrates the law of increasing opportunity cost. Its downward slope reflects scarcity. Figure 2.5 "Production Possibilities for the Economy.
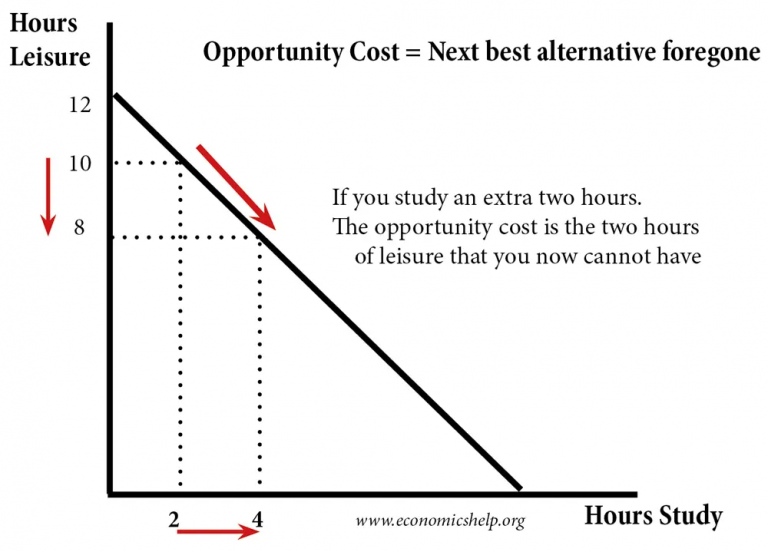
What is Opportunity Cost? Let's Take a Look at What it Means for You
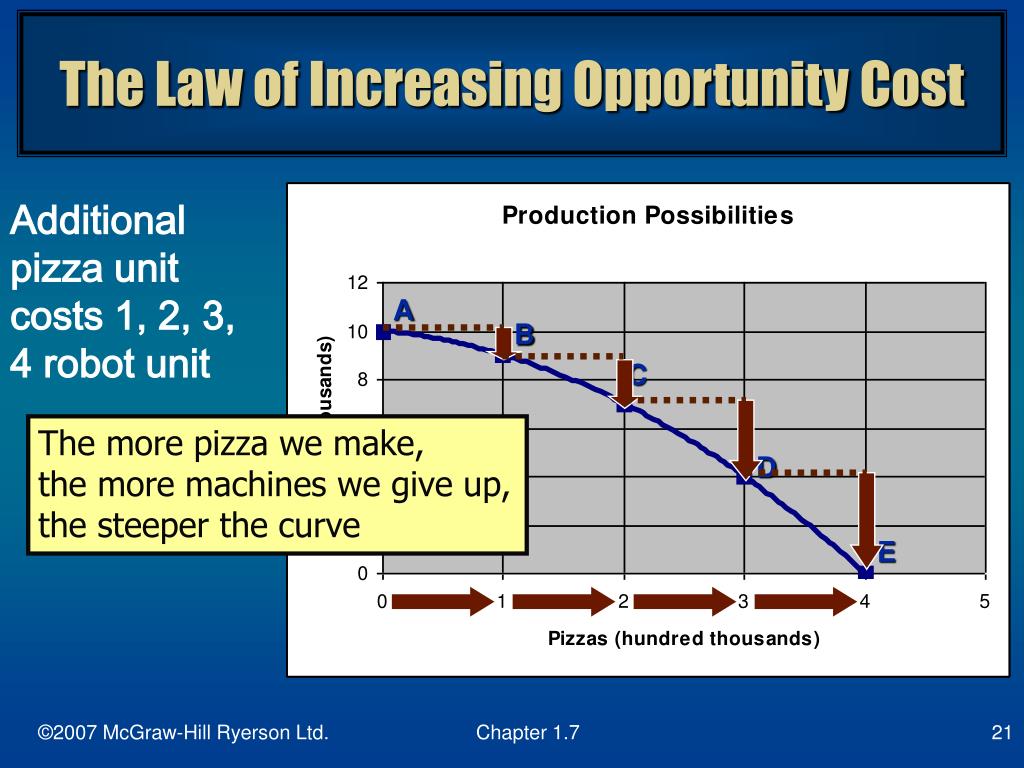
In this way, the law of increasing opportunity cost produces the outward-bending shape of the production possibilities frontier. Productive Efficiency and Allocative Efficiency. The study of economics does not presume to tell a society what choice it should make along its production possibilities frontier. In a market-oriented economy with a.
What is Opportunity Cost? Definition, Formula and Calculation Glossary
The law of increasing opportunity cost is an economic principle that describes how opportunity costs increase as resources are applied. (In other words, each time resources are allocated, there is a cost of using them for one purpose over another.). The law of increasing opportunity cost is an economic principle that describes how.
What is the law of increase opportunity cost? YouTube

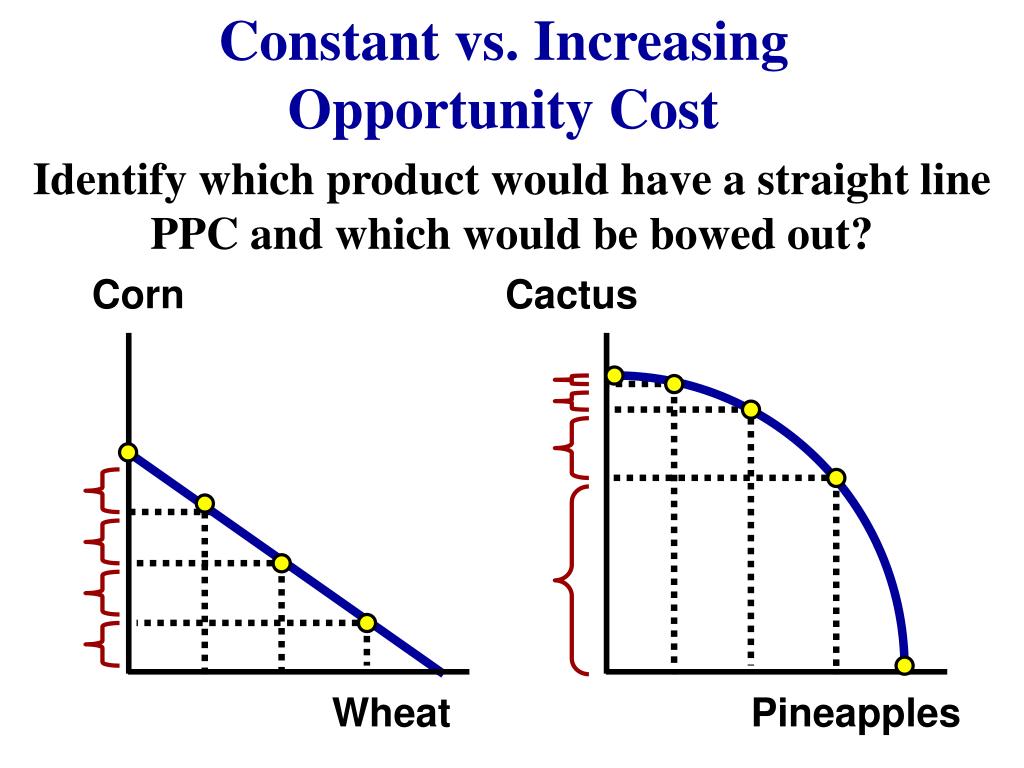
PPCs for increasing, decreasing and constant opportunity cost. We explore three different production possibility curves for the rabbits and berries example. Each curve has a different shape, which represents different opportunity costs. The bowed out (concave) curve represents an increasing opportunity cost, the bowed in (convex) curve.
PPT Economics The study of the allocation of scarce resources that
constant opportunity costs: when the opportunity cost of a good remains constant as output of the good increases, which is represented as a PPC curve that is a straight line; for example, if Colin always gives up producing 2 fidget spinners every time he produces a Pokemon card, he has constant opportunity costs. increasing opportunity costs
Opportunity Cost in Economics, Marginal Opportunity Cost Class 11 Notes
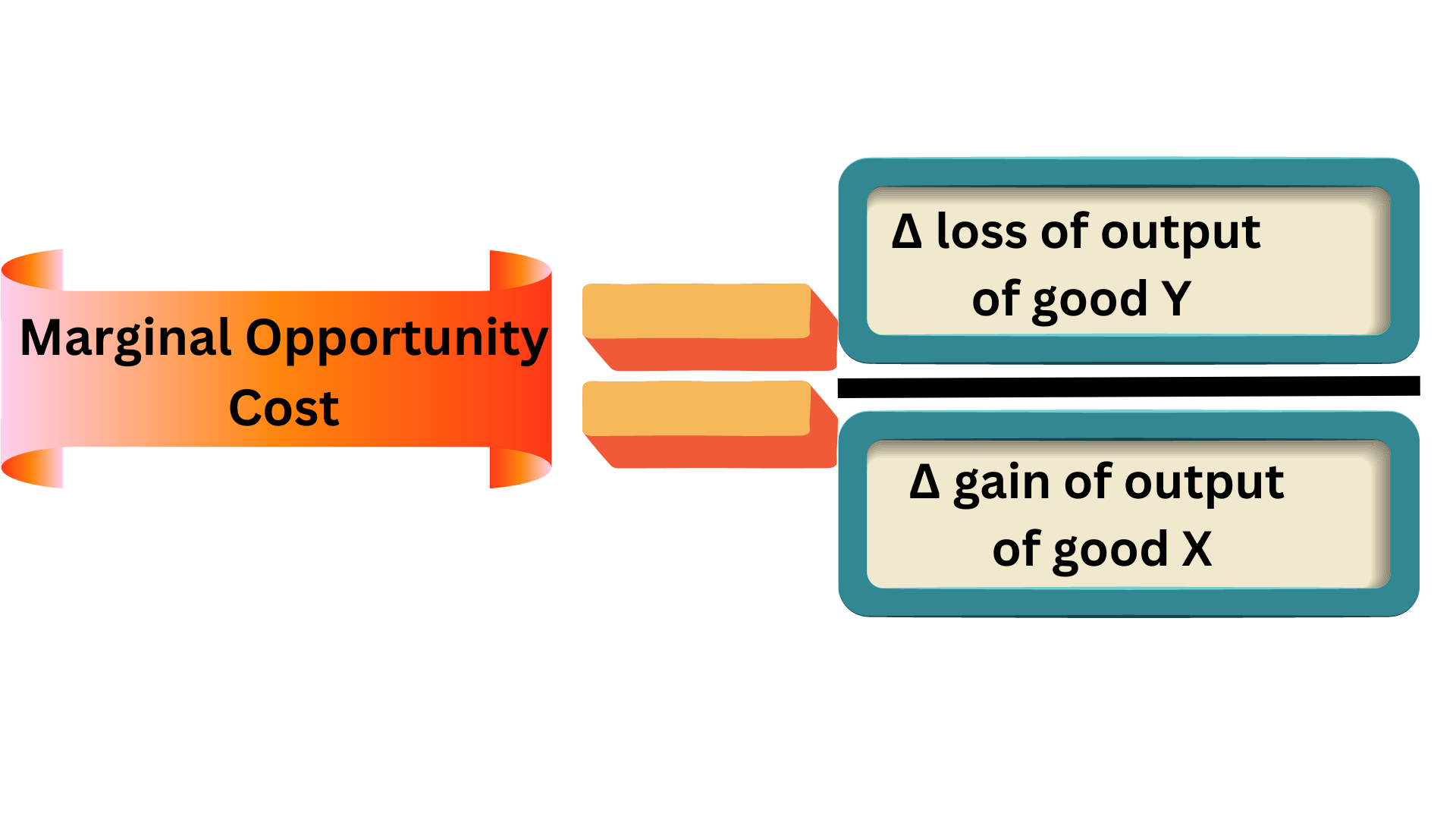
Lesson 5: The law of increasing opportunity cost: As you increase the production of one good, the opportunity cost to produce the additional good will increase. First, remember that opportunity cost is the value of the next-best alternative when a decision is made; it's what is given up. So let's compare straight and curved frontier lines to.
Economics Principles and Applications 2 e by Robert

In this way, the law of increasing opportunity cost produces the outward-bending shape of the production possibilities frontier. Productive Efficiency and Allocative Efficiency. The study of economics does not presume to tell a society what choice it should make along its production possibilities frontier. In a market-oriented economy with a.